The Science Behind Optimal MMT Knee Flexion Angle: A Comprehensive Guide
In this fast-paced world, it’s easy to take our bodies for granted. But what happens when even the simplest movements become a challenge?
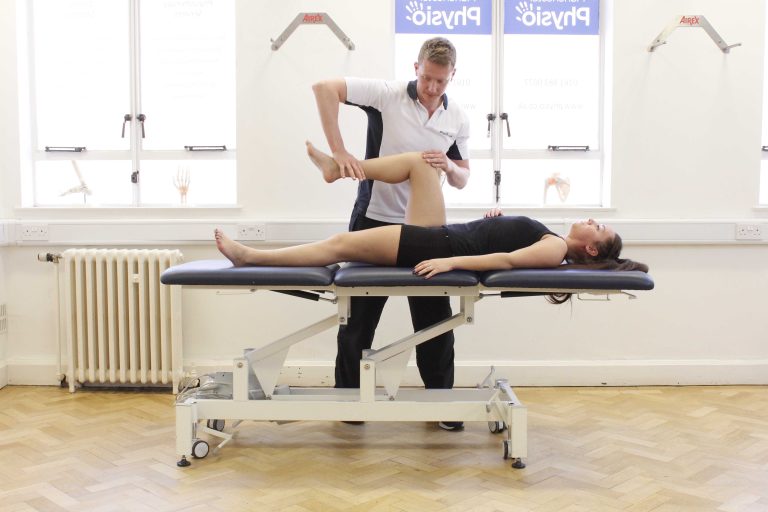
That’s where the magic of MMT knee flexion comes in. MMT, or Manual Muscle Testing, is a technique that allows us to assess the strength and function of our muscles.
Whether you’re an athlete striving for peak performance or someone looking to regain mobility after an injury, MMT knee flexion can unlock a world of possibilities. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of MMT knee flexion and discover the incredible potential of our bodies.
mmt knee flexion
MMT, also known as Manual Muscle Testing, is a method used by healthcare professionals to evaluate the strength and function of individual muscles or muscle groups. In the case of knee flexion, MMT is used to assess the strength of the muscles responsible for bending the knee.
During the test, the examiner applies resistance against the person’s attempt to flex their knee, evaluating their ability to overcome the resistance. By assessing knee flexion using MMT, healthcare professionals can gather important information about muscle strength and identify any weaknesses or imbalances that may be present.
Key Points:
- MMT is a method used to evaluate muscle strength and function.
- MMT assesses the strength of muscles responsible for bending the knee.
- Resistance is applied during the test to evaluate the person’s ability to flex their knee.
- MMT provides information about muscle strength and can identify weaknesses or imbalances.
- Healthcare professionals use MMT to gather important information about the knee flexion.
- MMT is a useful tool in assessing muscle strength and function in the knee.
Sources
https://www.physio-pedia.com/Manual_Muscle_Testing:_Knee_Flexion
https://www.kumc.edu/Documents/fshd/ManualMuscleTesting.pdf
https://www.niehs.nih.gov/research/resources/assets/docs/mmt8_grading_and_testing_procedures_for_the_abbreviated_8_muscle_groups_509.pdf
http://at.uwa.edu/mmt/knee.htm
Check this out:
💡 Pro Tips:
1. Gradual Progression: When working on knee flexion during manual muscle testing (MMT), it’s important to gradually increase the resistance or load applied to avoid straining the muscles. Start with a low level of resistance and progressively increase it as the patient demonstrates improved strength and control.
2. Stabilization Techniques: Proper stabilization of the patient’s leg during MMT knee flexion is crucial to isolate the muscles being tested. Use a sturdy surface or a stabilizing strap to secure the thigh to ensure accurate assessment of knee flexion strength.
3. Emphasize Eccentric Control: Besides measuring knee flexion strength, it is essential to assess the patient’s ability to control the movement in a slow and controlled manner during MMT. This eccentric control component is crucial for functional movements and injury prevention.
4. Mindful Breathing: Encouraging the patient to maintain relaxed and controlled breathing during MMT knee flexion can help promote better muscle activation and overall patient comfort. Instruct them to take deep breaths and exhale during the concentric phase of the movement.
6. Adequate Warm-up: Prior to performing MMT knee flexion, ensure the patient’s knee joint is adequately warmed-up to reduce the risk of injury. Simple warm-up exercises like knee extensions, light cycling, or dynamic stretches can help prepare the muscles and joints for the testing.
1. Introduction To Mmt Knee Flexion
Knee flexion refers to the bending movement that occurs at the knee joint, allowing the lower leg to move closer to the posterior thigh.
It is an essential component of many functional movements, such as walking, running, squatting, and climbing stairs. Maximum MMT (Manual Muscle Testing) knee flexion angle determines the extent to which the knee joint can flex and plays a crucial role in overall lower limb function and performance.
2. Importance Of Knee Flexion In Functional Movements
Knee flexion is fundamental for everyday movements, from simple tasks like walking to more complex activities like sports.
Understanding the importance of knee flexion in functional movements helps us recognize its significance and the implications of any limitations or weaknesses in this movement. Some key points to consider include:
-
Knee flexion allows for efficient walking and running gait cycles, facilitating forward movement and propelling the body forward. – Adequate knee flexion is essential for optimal lower limb biomechanics during activities such as squatting, lunging, and jumping.
-
Insufficient knee flexion can compromise balance, stability, and agility, increasing the risk of falls and other related knee injuries. – Restrictions in knee flexion may lead to compensatory movements in other joints, potentially causing biomechanical imbalances and overuse injuries.
3. Benefits Of Mmt Knee Flexion
Achieving optimal MMT knee flexion angle offers numerous benefits, including:
-
Improved lower limb strength and power: Increasing knee flexion allows for enhanced muscle recruitment and force production, leading to improved lower limb strength and power. – Enhanced athletic performance: Adequate knee flexion range of motion is necessary for optimal performance in sports that involve jumping, cutting, and sprinting.
-
Injury prevention: Maintaining adequate knee flexion mobility, along with strength and stability, can help prevent knee injuries such as strains, tears, and patellofemoral pain syndrome. – Functional daily activities: Optimal knee flexion range ensures the ability to perform a wide range of functional activities with ease, such as walking, climbing stairs, and sitting down and standing up from a chair.
4. Techniques For Assessing Knee Flexion Strength
To accurately assess knee flexion strength, several techniques can be employed:
-
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT): This involves a trained professional applying resistance to the knee joint as the individual attempts to flex the knee against the resistance. The strength is then graded on a scale, providing an indication of the individual’s knee flexion strength.
-
Isokinetic Testing: Isokinetic machines can assess the peak torque produced by the knee muscles during flexion movement. This measurement provides a quantitative assessment of knee flexion strength.
-
Functional Movement Tests: Functional movements such as squatting, lunging, and step-ups can also be used to assess knee flexion strength indirectly by evaluating the individual’s ability to perform these movements efficiently and without compensation.
5. Exercises To Improve Mmt Knee Flexion
To improve MMT knee flexion, the following exercises can be incorporated into a training program:
-
Hamstring Stretching: Stretching exercises targeting the hamstrings, such as standing hamstring stretches and lying hamstring curls with a resistance band, can help improve knee flexion range of motion. – Quadriceps and Hip Flexor Strengthening: Strengthening exercises for the quadriceps and hip flexor muscles, such as squats, lunges, and leg press, can contribute to improved knee flexion strength.
-
Closed Chain Exercises: Closed chain exercises, such as step-ups, split squats, and pistol squats, engage multiple muscle groups and promote knee flexion strength development. – Plyometric Training: Plyometric exercises, including box jumps and lateral bounds, can enhance both knee flexion strength and power, particularly in athletes.
6. Precautions And Considerations For Mmt Knee Flexion Training
While training MMT knee flexion, it is important to consider the following precautions:
-
Gradual Progression: It is crucial to progress gradually and avoid sudden overload to prevent muscle strains and joint stress. Gradually increase intensity, load, or volume of exercises over time.
-
Proper Form and Technique: Maintaining proper form and technique during exercises is essential to ensure optimal muscle recruitment and prevent injury. Seek guidance from a qualified fitness professional or physical therapist if unsure.
-
Individualization: Consider individual differences in terms of pre-existing knee conditions, injury history, and overall fitness level. Tailor exercises and training programs accordingly to cater to individual needs.
-
Warm-Up and Cool-Down: Prioritize a thorough warm-up routine that includes dynamic stretches to prepare the muscles and joints for exercise. A cool-down routine should also be implemented to promote recovery and prevent muscle tightness post-training.
In conclusion, understanding the science and importance of MMT knee flexion angle is crucial for optimizing lower limb function and preventing knee injuries. By assessing knee flexion strength, incorporating specific exercises, and following appropriate precautions, individuals can improve their knee flexion range, strength, and overall functional performance.