Psoas vs Iliopsoas Muscle: Understanding Their Roles and Functions
In the intricate world of our musculoskeletal system, there is a pair of muscles that often fly under the radar but play a crucial role in our daily movements. Meet the psoas and iliopsoas muscles, an inseparable duo responsible for flexing and externally rotating our thighs, as well as maintaining the graceful curve of our lower backs.
So, why should these hidden heroes matter to you? Well, imagine a life with constant hip pain and limited mobility, where the simplest of tasks become a challenge.
In this article, we will delve into the secrets of the psoas vs iliopsoas muscles, unraveling their importance and exploring effective ways to keep them in top-notch condition.
psoas vs iliopsoas muscle
The psoas and iliopsoas muscles are closely related and often used interchangeably, but there are some differences between the two. The iliopsoas muscle is actually composed of two muscles, the iliacus and the psoas major.
The main function of the iliopsoas muscle is to flex and externally rotate the thigh at the hip joint and flex the trunk at the hip. The psoas major muscle can also act independently on the lumbar spine.
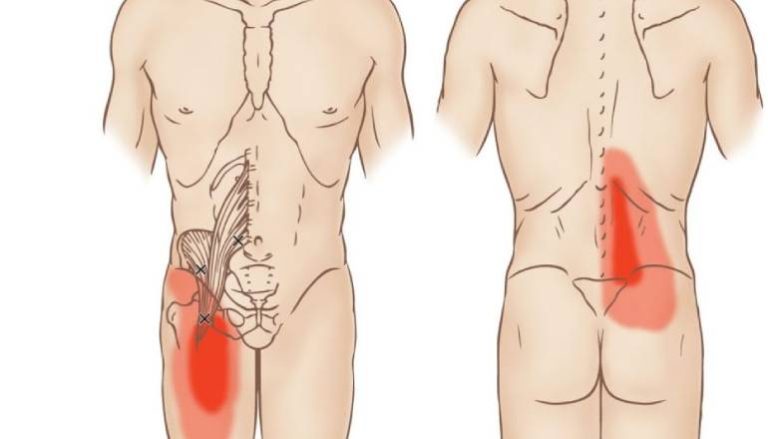
Additionally, the iliopsoas muscle maintains normal lumbar lordosis during standing and acts as an antagonist to the gluteus maximus and hamstring muscles. Injury to the iliopsoas muscle can cause hip pain and limited mobility, and conditions associated with the muscle include tendonitis, bursitis, and snapping hip syndrome.
Weakness in the iliopsoas muscle may occur due to lumbar injuries, and proper alignment, muscular balance, and flexibility of the muscle are important for preventing pain and dysfunction. Rehabilitation may involve rest, gentle stretches, strengthening exercises, lumbar stretches, and heat or ice application.
It is recommended to consult with a physician and physical therapist before starting treatment for an iliopsoas injury. The effectiveness of treatments such as psoas massage compared to stretching and strengthening exercises is debated, so individualized care is essential.
Key Points:
- The psoas and iliopsoas muscles are closely related, but there are some differences between the two.
- The iliopsoas muscle is composed of two muscles, the iliacus and the psoas major.
- The main function of the iliopsoas muscle is to flex and externally rotate the thigh at the hip joint and flex the trunk at the hip.
- The psoas major muscle can also act independently on the lumbar spine.
- Injury to the iliopsoas muscle can cause hip pain and limited mobility, and conditions associated with the muscle include tendonitis, bursitis, and snapping hip syndrome.
- Rehabilitation for an iliopsoas injury may involve rest, gentle stretches, strengthening exercises, lumbar stretches, and heat or ice application.
Sources
https://www.verywellhealth.com/iliopsoas-anatomy-4706830
https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/iliopsoas-muscle
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535418/
https://wikidiff.com/psoas/iliopsoas
Check this out:
💡 Pro Tips:
1. The iliopsoas muscle can become tight and shortened due to prolonged sitting or a sedentary lifestyle. Regular stretching and mobility exercises can help prevent this and maintain flexibility in the muscle.
2. Strengthening the gluteus maximus and hamstring muscles can help balance the strength and function of the iliopsoas muscle, reducing the risk of injury or dysfunction.
3. Avoid excessive or repetitive hip flexion movements, such as long-distance running or high-impact activities, to prevent strain on the iliopsoas muscle.
4. Incorporating exercises that target core stability, such as planks and deadlifts, can help improve the coordination and strength of the iliopsoas muscle, as it works in conjunction with the abdominal muscles for trunk stabilization.
5. If experiencing chronic hip pain or limited mobility, seeking a professional evaluation from a healthcare provider who specializes in musculoskeletal or sports medicine can help identify any specific issues related to the iliopsoas muscle and determine appropriate treatment options.
1. Functions Of The Iliopsoas Muscle
The iliopsoas muscle is a complex muscle composed of the iliacus and psoas major muscles, which originate from different locations but merge to form a single tendon that inserts on the femur. This muscle plays a crucial role in various movements and functions in the body.
– Flexion and External Rotation of the Thigh: One of the primary functions of the iliopsoas muscle is to flex and externally rotate the thigh at the hip joint. This movement is essential for activities such as walking, running, and climbing stairs.
– Flexion of the Trunk at the Hip: The iliopsoas muscle also contributes to the flexion of the trunk at the hip joint. This movement is commonly seen when lifting the legs while lying flat on the back or performing sit-ups.
– Independent Action on the Lumbar Spine: Interestingly, the psoas major muscle, which is a part of the iliopsoas muscle, can also act independently on the lumbar spine. It helps stabilize and control movements of the lower back.
– Maintenance of Lumbar Lordosis: The iliopsoas muscle is responsible for maintaining normal lumbar lordosis, the inward curvature of the lower back. It acts as an antagonist to the gluteus maximus and hamstring muscles, helping to balance the forces acting on the hip and pelvis.
2. Impact Of Injury On The Iliopsoas Muscle
Injury to the iliopsoas muscle can result in hip pain and limited mobility. This can significantly affect an individual’s daily activities and quality of life.
Some common causes of iliopsoas muscle injury include overuse, sudden trauma, repetitive strain, and direct blows to the hip region.
People experiencing iliopsoas muscle injury may notice symptoms such as:
3. Innervation Of The Iliacus And Psoas Major Muscles
The iliacus muscle, which is part of the iliopsoas muscle, is innervated by the femoral nerve. This nerve arises from the lumbar plexus and provides sensory and motor innervation to the muscles of the anterior thigh.
On the other hand, the psoas major muscle receives its innervation from the lumbar plexus, specifically from the ventral rami of the lumbar spinal nerves (L1-L3). This dual innervation allows the iliopsoas muscle to execute its various functions effectively.
4. Conditions Related To The Iliopsoas Muscle
Several conditions can arise in relation to the iliopsoas muscle. It’s important to be aware of these conditions to seek appropriate treatment and prevent further complications:
– Iliopsoas Tendonitis: This condition refers to inflammation and irritation of the iliopsoas tendon. It typically occurs due to repetitive overuse, trauma, or muscular imbalances.
Symptoms may include pain, tenderness, and swelling in the hip or groin area.
– Iliopsoas Bursitis: Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints. When the bursa located near the iliopsoas muscle becomes inflamed, it leads to iliopsoas bursitis.
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and difficulty with leg movements.
– Snapping Hip Syndrome: This condition causes a snapping or popping sensation in the hip joint, often accompanied by pain. Snapping hip syndrome can occur when the iliopsoas tendon or other soft tissues rub against bony structures in the hip, leading to irritation and discomfort.
5. Weakness In The Iliopsoas Muscle And Its Causes
Weakness in the iliopsoas muscle can result from various factors, including:
– Lumbar Injuries: Conditions such as herniated discs or lumbar facet arthritis can impact the function of the iliopsoas muscle. Nerve impingement or damage in the lumbar region can weaken the muscle and hinder its ability to perform effectively.
– Muscle Imbalances: Weakness in certain muscles, such as the gluteus maximus or hamstrings, can create imbalances and affect the function of the iliopsoas muscle. This can lead to compensatory movements and weakness in the hip.
6. Rehabilitation And Treatment Options For Iliopsoas Injuries
Rehabilitation of iliopsoas injuries involves a comprehensive approach focused on eliminating pain, restoring strength, and improving mobility. Treatment options may vary depending on the severity of the injury, and consultation with a physician and physical therapist is highly recommended.
Rehabilitation strategies for strengthening and recovering the iliopsoas muscle may include:
It’s worth noting that psoas massage as a treatment option for iliopsoas injuries is a debated subject, and its effectiveness compared to stretching and strengthening exercises is questionable. Therefore, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the individual’s specific condition.
In conclusion, understanding the functions, impacts of injury, innervation, and treatment options for the iliopsoas muscle is crucial for maintaining optimal hip health. Proper alignment, muscular balance, and flexibility are vital to prevent pain and dysfunction in the hip region.
If experiencing any symptoms or discomfort related to the iliopsoas muscle, seeking professional advice is essential for an accurate diagnosis and effective rehabilitation plan.